Archaeologists in Cambodia have unearthed the torso of a Buddha statue at the ancient Angkor temple complex, a discovery hailed as a significant find.
The torso, believed to date back to the 12th or 13th century, remarkably matches a head discovered at the same site nearly a century ago.
The discovery was made last month during an excavation at Ta Prohm temple by a joint team of Cambodian and Indian archaeologists.
The team unearthed the torso, standing at 1.16 metres (3 3/4 feet) tall, along with 29 other fragments believed to be part of the same statue. The statue is crafted in the Bayon art style, characteristic of the renowned Bayon temple within the Angkor complex.
Archaeologist Neth Simon, speaking from Siem Reap province, expressed surprise at the discovery. “It was a big surprise when we unearthed this sculpture because all we’d found so far were small pieces,” she said.
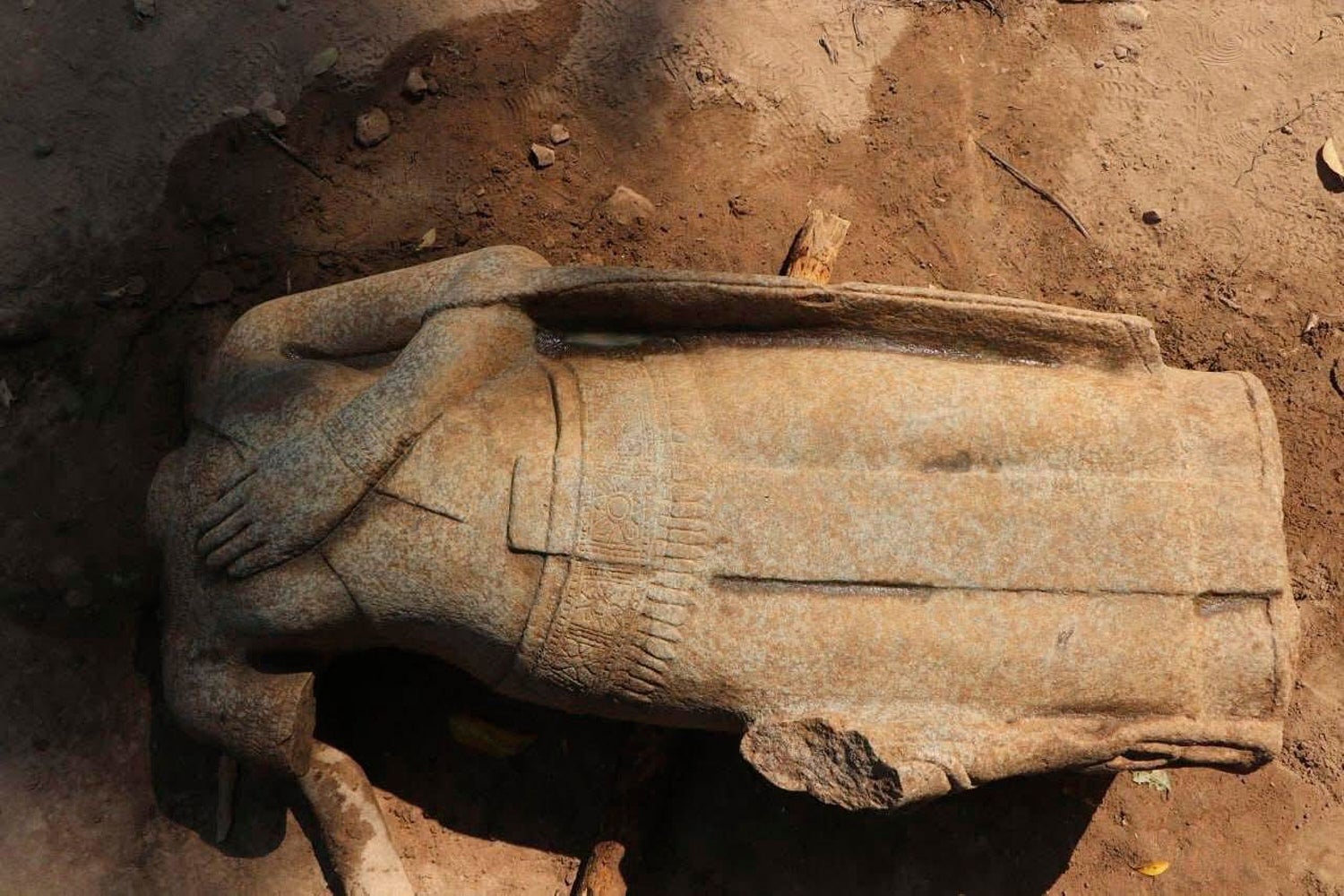

She described the statue’s design as displaying carved jewellery and robe and sash, with a unique left-hand gesture across the chest — “an uncommon representation in Khmer (Cambodian) art.”
The statue’s presumed head was discovered at the same temple in 1927 during the French colonial era, and is currently kept at Cambodia’s main National Museum in the capital Phnom Penh. Neth Simon said the torso was found about 50 metres away from the site where the head was discovered, and that an optical electronic scan confirmed they were a match.

A near-complete reconstruction of the statue is possible, Neth Simon added, now that only the right hand of the statue remains missing. Her team will ask the Minister of Culture and Fine Art for approval to reattach the head and body of the sculpture to make it whole for public display.
The Angkor site sprawls across some 155 square miles, containing the ruins of capitals of various Cambodian empires from the 9th to the 15th centuries. Scholars consider it to be one of the most important archaeological sites in Southeast Asia.
The site is Cambodia’s most popular tourist attraction and in 2024 attracted about a million international tourists, according to Cambodia’s Tourism Ministry.
The excavations aim to organise and preserve the numerous art objects scattered throughout the Ta Prohm complex, highlighting the ongoing efforts to protect and understand Cambodia’s rich cultural heritage, the Apsara Authority says.
Neth Simon said she would be delighted if the statue’s pieces could be reassembled after being far apart from each other for a century.
“As an archaeologist, I would be really happy,” she said.